How Do Chemists Model the Valence Electrons in Metal Atoms
The valence electrons of metal atoms can be modeled as a sea of electrons. How do chemists model the valence electrons in metal atoms.

What Are Valence Electrons Chemtalk
To determine the valence electrons in nitrogen N you must count the electrons in the highest energy level n 2 thus count the electrons in the 2s and 2p orbitals.

. Depending on in this nature of elements can be a metal non-metal or a metalloid. The electrons are free to move throughout this electron sea. The simplest and most accurate way to determine the valence electron is to know in detail the electron configuration of that element.
If you do the valence electrons of N is 5. To find the number of valence electrons in an atom of a representative element simply look at its group number. How do electrons behave in metals.
Why are alloys more useful than pure metals. In this model the valence electrons are free delocalized and mobile. The electron configuration shows that the last shell of iron has two electrons and the d-orbital has a total of six electrons.
This time we will see how to arrange the electrons of an element. Alloys are important because their properties are often superior to those of their component elements. Metallic bonds are the forces of attraction between the free-floating valence electrons and the positively charged metal ions.
However metal have great tendency to release valence electrons mostly due to less effective nuclear charge among all the elements in a period and inc. The valence electrons of an element can be found out by. Valence electrons can not be accurately determined by block and group.
The s and p valence electrons of metals are loosely held. Alloys are important because their properties are often superior to those of their component elements. For the transition element the valence electrons have to be determined by adding the total electrons of the d-orbital to the electrons in the last orbit of the atom.
Valence electrons are outermost electrons which are present in the outermost shell of any atomMay it be metal or non metal or metalloid. That is to say instead of orbiting their respective metal atoms they form a sea of electrons that surrounds the positively charged atomic nuclei of. The valence electrons of metal atoms can be modeled as a sea of electrons.
These valence electrons hold the positive ions together throughout the structure of the metal. Valence electrons are electrons that occupy the highest energy level. The key characteristics exhibited by valence electrons are as follows.
The Electron Sea Model. This model proposes that all the metal atoms in a metallic solid contribute their valence electrons to form a sea of electron. A closed shell of valence electrons ie eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom will.
But valence electrons can be easily identified by electron configuration. The valence electron for the main group elements exists only in the outermost electron shell. For a transition metal a valence electron can exist in the inner shells also.
The electrons present in the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are not held by any specific. The valence electrons of atoms in a pure metal can be modeled as a sea of electrons. The valence electrons of atoms in a pure metal can be modeled as a sea of electrons.
In metallic bonds the valence electrons from the s and p orbitals of the interacting metal atoms delocalize. Metallic bonds do not involve the sharing of electrons. To determine the number of valence electrons in any type of atom find the element on the periodic table and count across that row from the left side as done in the examples below.
One of the easiest ways to find valence electrons is by checking out the elements place in the periodic table. Determination of Valence Electrons. Why are alloys more useful than pure metals.
But the valence electrons of the transition elements are located in the inner orbit. Lets use this idea to create a model of metallic bonding to. The electrons then move freely throughout the space between the atomic nuclei.
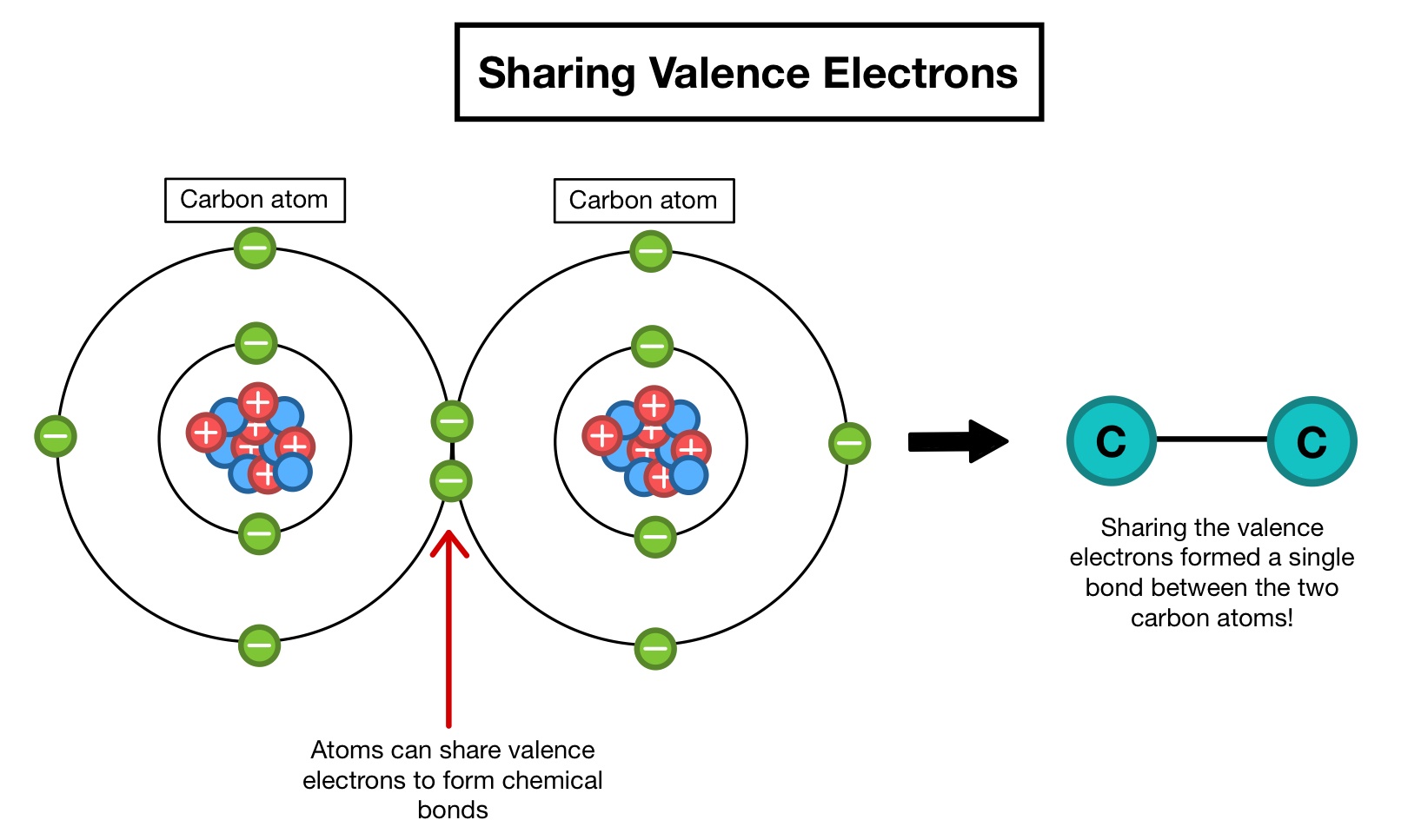
That is the valence electrons are mobile and can drift freely from one part of the metal to another. Valence electrons are involved in the formation of chemical bonds between atoms so it is helpful for chemists to know how many valence electrons each type of atom has. Which of these describes the arrangement of particles in a metal.
These electrons are usually available to combine bond with other atoms. In metallic bonds the valence electrons from the s and p orbitals of the interacting metal atoms delocalize. This forms a sea of electrons that surrounds the metal cations in the solid.
So how does this arrangement allow metals like copper or aluminum wires conduct and carry electricity to our homes. Valence electrons also determine the electrical conductivity of an element. The nature of metals and metallic atoms is that they have loosely held electrons that can be taken away fairly easily.
Generally the valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell in other words the last electrons addedFor reasons that are a little too complex to explain here when electrons are added to the outermost d shell of a transition metal more on this below the first electrons that go into the shell tend to act like normal valence electrons but after that they dont and. Positive atomic nuclei surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons the blue dots. In a metallic solid atoms are arranged in a lattice-like 3D structure where there is a regular array of metal cations surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons.
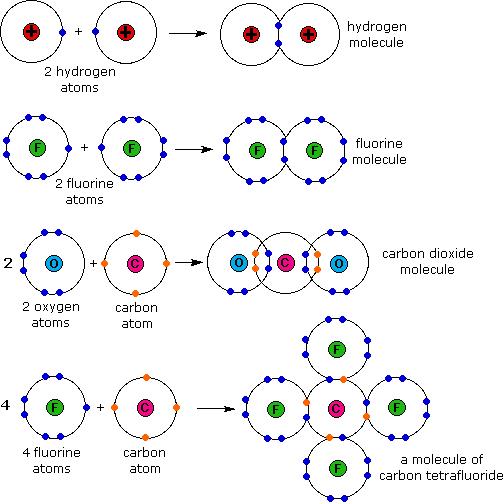
Electron dot structures diagrams that show valence electrons in the atoms of an element as dots. Metals are able to conduct electricity because atoms of metals easily lose their valence electrons to become positively charged ions. They leave their own metal atoms.
Valence Electrons Definition Importance Expii
Electron Configurations The Periodic Table

How Many Valence Electrons Does Aluminum Al Have In 2022 Electrons Electron Configuration Ionic Bonding
No comments for "How Do Chemists Model the Valence Electrons in Metal Atoms"
Post a Comment